What Is Cloaking?

Cloaking is a technique used in online marketing and traffic management to display different content to users and platforms. While cloaking is often discussed in the context of SEO, its applications extend beyond search engines to advertising networks and affiliate marketing.
- How Does Cloaking Work?
- Applications of Cloaking in Digital Marketing
- Content Moderation Types
- Tools and Techniques for Effective Cloaking
- Risks and Challenges
- Real-World Examples of Cloaking
- FAQ
- Conclusion
How Does Cloaking Work?
At its core, cloaking involves presenting different versions of a webpage or ad depending on the visitor’s characteristics. This is achieved through the collection and analysis of various visitor parameters:
- User-Agent – a browser identification string containing information about the device and operating system used.
- IP Address – a unique network address that helps determine geolocation, ISP, and potential use of VPN or proxy.
- JavaScript Parameters – a set of browser characteristics, such as screen resolution, fonts, installed plugins, and many other attributes.
- HTTP_REFERER – a request header indicating which website or page the visitor came from.
- Accept-Language – a browser parameter that provides information about the user's preferred language.
- UTM Tags – tracking parameters that include campaign identifiers, allowing traffic sources to be monitored. For example, gclid, which is present in all visitors from Google Ads.
- Time Zone – information about the time zone of the visitor's device.
- Touch Screen – a parameter that determines whether the user's device has a touchscreen.
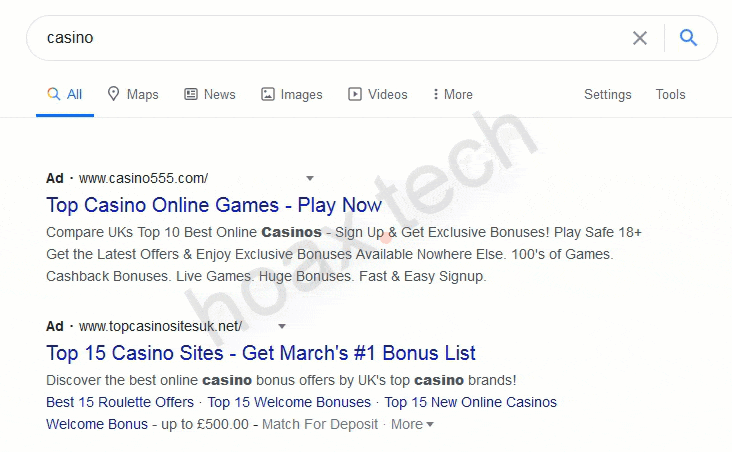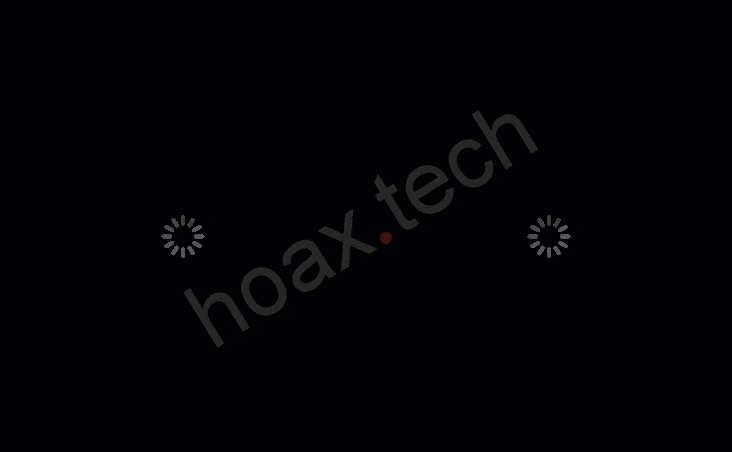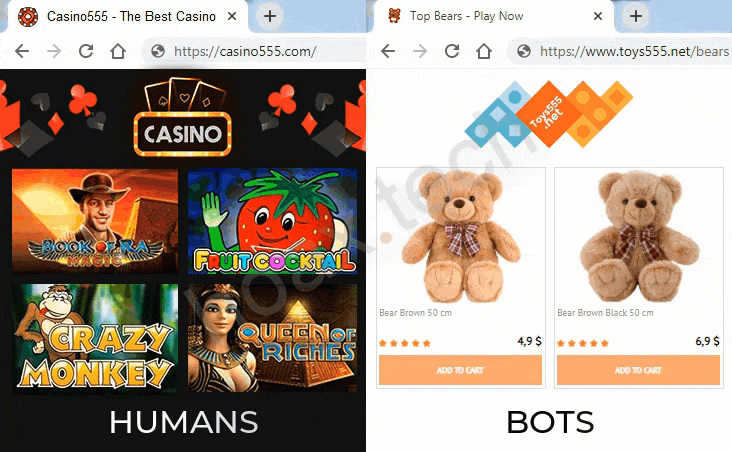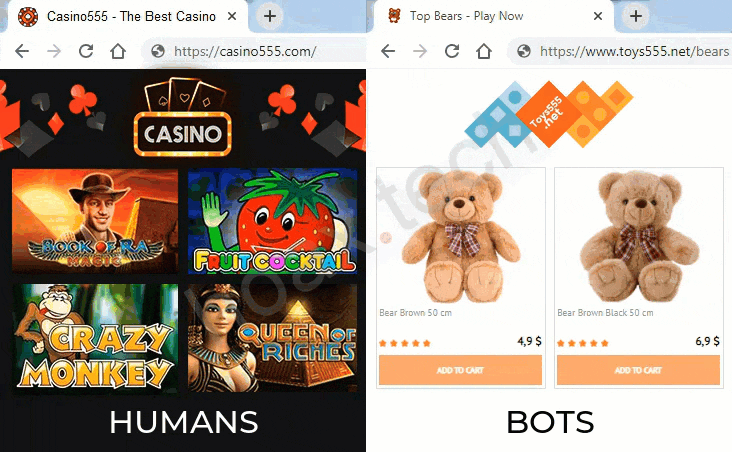
These filters and verification methods work together to determine whether a visitor is a bot, a moderator, or a genuine user from the target audience. Based on this analysis, cloaking service decides whether to keep the visitor on a safe page with neutral content (so-called "white page") or redirect them to a page featuring a restricted offer that might not comply with advertising network’s policies (the "black page").

Applications of Cloaking in Digital Marketing
Cloaking is used across various industries, each with its own purpose and implementation methods:
- SEO Cloaking – Used to manipulate search rankings by showing search engine crawlers content different from what users see. This technique helps rank pages higher while delivering optimized content to visitors.
- Affiliate Marketing – Cloaking allows affiliates to promote offers that might otherwise be flagged by ad networks. For example, when a user clicks on an ad for a weight loss supplement, bots and moderators are shown a neutral health and wellness blog, while real users are redirected to a landing page with the actual weight loss product offer.
- Email Marketing – Used to bypass email service filters by cloaking links in emails. Bots scanning email content see a safe, compliant version, while real recipients receive the intended promotional content.
- SMS Marketing – Similar to email cloaking, it disguises links in text messages to avoid spam filters. Message scanners detect neutral content, while users receive targeted promotional links.
- Protecting Ad Links from Competitors – Prevents rival marketers from copying or reporting ad links by displaying different URLs depending on the visitor type. This ensures traffic reaches the intended audience without interference.
- Cybersecurity and Fraud Prevention – Used to mislead malicious bots and hackers by serving decoy content, preventing scraping, data theft, or automated attacks.
Each of these applications demonstrates how cloaking is a versatile tool, balancing strategic advantage with the challenges of platform compliance.
Content Moderation Types
Content moderation in advertising networks generally falls into two main categories:
- Automated Moderation – This is the primary method, accounting for around 99% of all reviews. When a link is added to an ad campaign it first goes through an automated review to check for prohibited or harmful content. AI-driven bots scan texts, images, and files associated with the promoted website. If the content meets the platform’s guidelines, the campaign is approved and goes live.
- Manual Moderation – In some cases, ads undergo manual review. On major platforms like Google Ads and Facebook Ads, this often happens after a certain spending threshold is reached. In smaller ad networks with fewer advertisers, manual moderation may be applied to every campaign. This process can take several days. In such networks, advertisers often use temporary full white page displays during moderation to ensure approval.
In both cases, cloaking ensures that bots and moderators see a safe, compliant page. However, during manual moderation, the quality of the white page becomes crucial, as it is evaluated by a human reviewer rather than an automated system.
Tools and Techniques for Effective Cloaking
To implement cloaking successfully, marketers rely on advanced cloaking services that can:
- Detect bot traffic and ad network moderators.
- Segment audiences based on behavior and geolocation.
- Redirect visitors dynamically based on pre-set rules.
Risks and Challenges
While cloaking provides strategic advantages, it also carries risks:
- Ad Account Bans – Platforms like Google Ads, Facebook Ads, and TikTok Ads strictly prohibit cloaking. If detected, an account may be permanently banned. Additionally, users often report aggressive ads promoting restricted content, increasing the likelihood of account suspension. Ad networks are increasingly using AI to detect cloaking patterns.
- Traffic Loss – Incorrectly configured cloaking filters can result in losing valuable traffic. Users with strict browser security settings or those using devices with unusual characteristics may be mistakenly identified as bots and left on the white page instead of reaching the intended offer.
- Loss of Search Rankings – SEO cloaking can lead to severe penalties from search engines. If detected, the website may not only lose its rankings but also be removed from the index, resulting in a drop in organic traffic.
Real-World Examples of Cloaking
- Gambling – Casino advertising is banned in many countries, and even where it's allowed, a license is often required for promotion. To bypass restrictions and avoid ad network bans, affiliates use cloaking for gambling offers.
- Crypto – Advertising for cryptocurrency projects is heavily restricted or outright banned on platforms like Google Ads, making cloaking a common strategy for affiliates in this niche.
- Weight Loss – The weight loss vertical is under strict scrutiny due to claims of misleading promises and potential side effects. Cloaking is widely used to promote dietary supplements, meal plans, and other weight loss products while avoiding ad rejections.
- Finance – Financial products, such as forex trading, loans, and microcredit services, face strict advertising regulations on major platforms. Affiliates rely on cloaking to ensure their promotions reach the target audience.
- E-commerce – Dropshipping stores often use aggressive advertising tactics that may violate platform policies. Cloaking helps affiliates keep their campaigns running without constant ad disapprovals.
FAQ
1. Is cloaking illegal?
Cloaking itself is not illegal, but it violates the policies of many advertising platforms, including Google and Facebook. If detected, your accounts may be banned.
2. How do companies detect cloaking?
Ad networks use AI-driven crawlers, IP tracking, and behavioral analysis to identify cloaking patterns.
3. Can cloaking be used ethically?
Some forms of cloaking, such as geo-targeting and personalized content delivery, are considered ethical. However, misleading search engines or ad platforms is not allowed.
4. What is the safest way to use cloaking?
Using advanced filtering tools and ensuring compliance with local regulations can help reduce risks associated with cloaking.
5. Are there any alternatives to cloaking?
Alternatives include running compliant ads, using pre-landers, and leveraging native advertising networks that allow more flexibility in ad content.
Conclusion
Cloaking is still a powerful tool in affiliate marketing and other niches. However, it requires caution and ongoing risk management. Besides cloaking services, affiliate marketers need to use high-quality, safe pages and create ads that are relevant to the white page. When done right, cloaking can significantly boost campaign performance and take an arbitrage marketer's earnings to the next level.